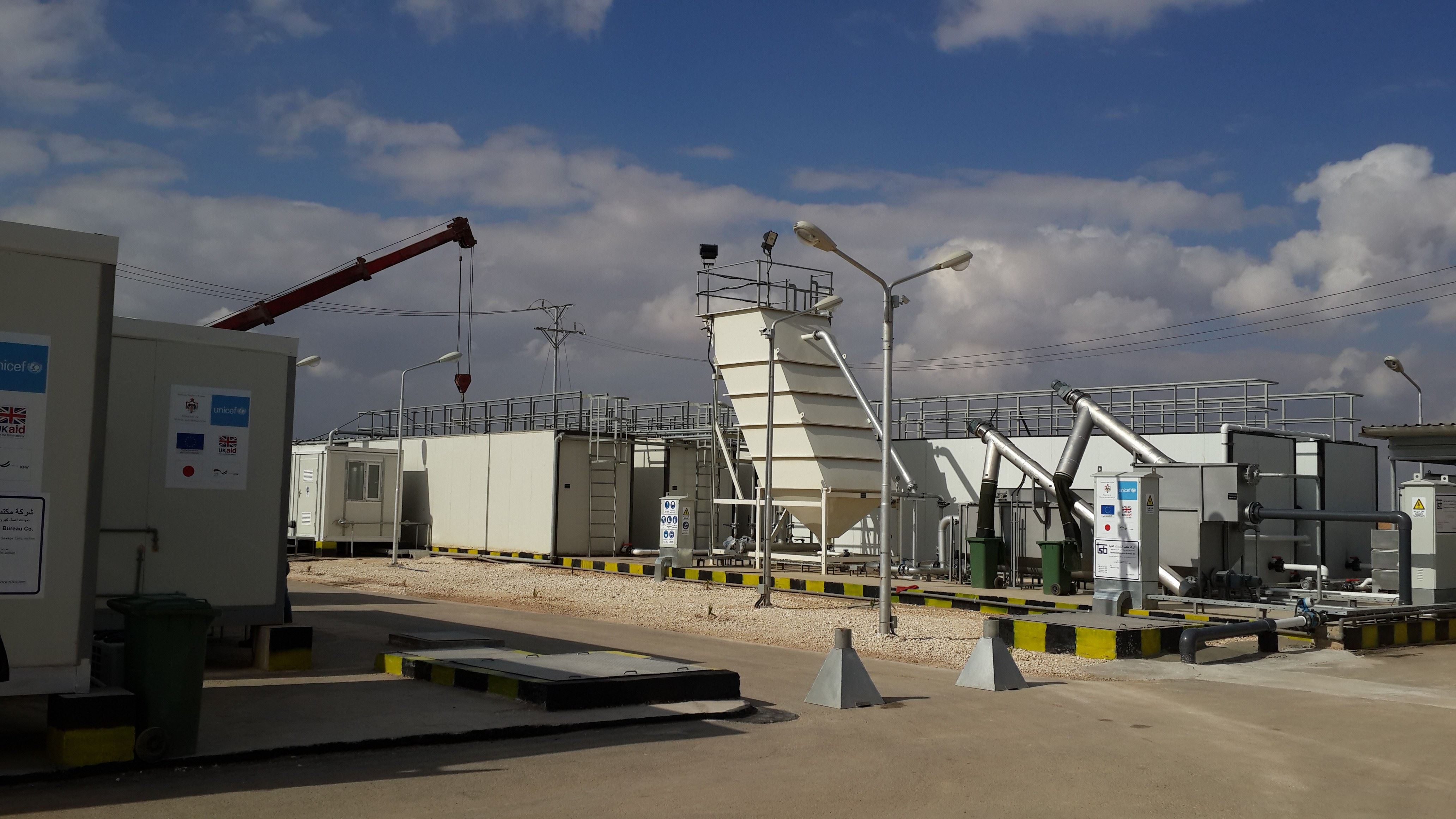
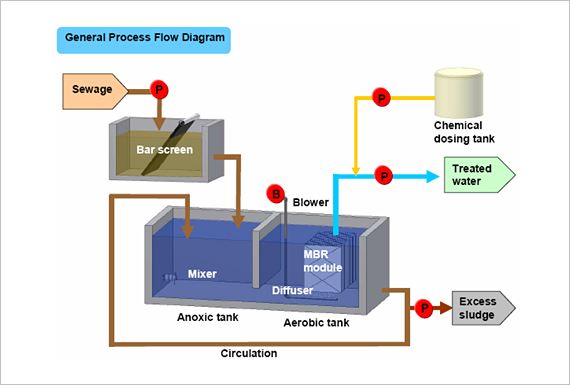
MBR-Membrane Bio-Reactor
This technology is a combination of membrane process like microfiltration, nanofiltration, ultrafiltration with biological waste water treatment process i.e. ASP (ACTIVATED SLUDGE PROCESS). It is one of the most important innovation in waste water treatment as it overcome the drawbacks of the conventional ASP, including large space requirement for secondary clarifiers, liquid–solid separation issues, production of excess sludge, and limitations with removal of recalcitrant. Its claimed ability to hold and sustain mixed liquor suspended solids (MLSS) of three to four times than what is possible in the conventional aeration tanks which in turn offers minimization of the footprint of the treatment plant. Diffused aeration is of course needed. The membrane is a matter of proprietorship and the throughput per membrane module offered by various vendors are different and also each vendor advocates various shapes of the membranes as flat sheet, cross flow, dead end flow etc, which makes it difficult for common validated standard design criteria.
MBR is available in two configuration
1.Internal/ Submerged- In this configuration the filtration element is installed in the main bioreactor vessel or in any separate tank. The membrane can be a combination of tubular and flat sheet and an online backwash system ca be incorporated which can reduce membrane surface fouling umping membrane permeate back through the membrane. 2. External/Side stream- In this configuration filtration element are installed externally to the reactor. Membrane modules are arranged in series through which biomass is pumped to the bioreactor or bank modules.






Major Consideration in MBR-
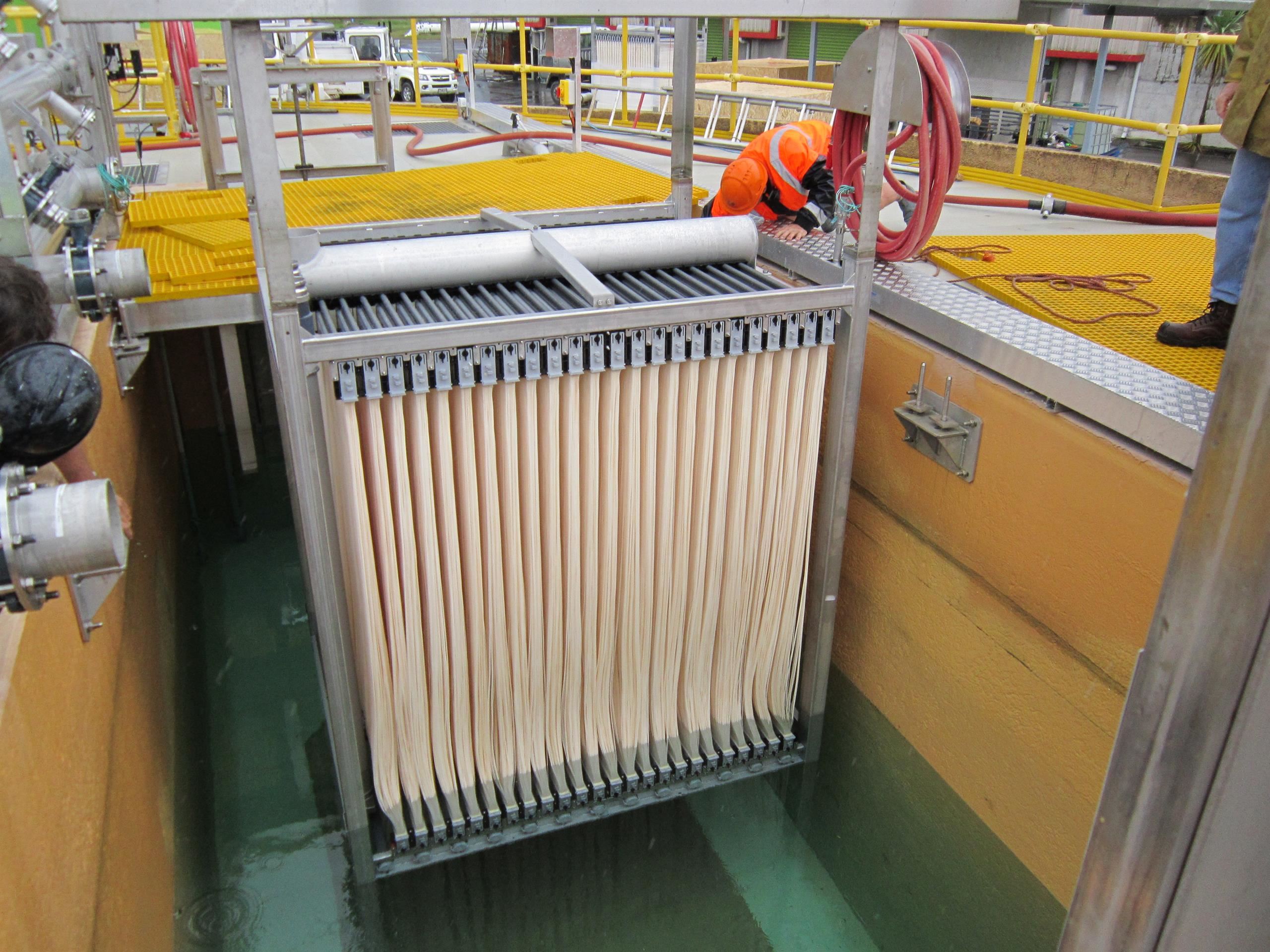
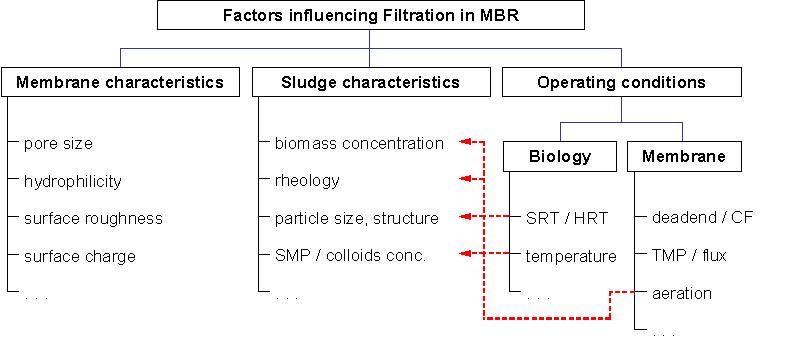
Membrane Fouling & Fouling Control- The major drawback of this system is of membrane fouling due to the deposition of insoluble and particulate materials onto and into the membrane. Due to this membrane performance inevitably decreases with filtration time. It affects the system performance & operating cost of plant
Advantages
-
High quality effluent for reuse without separate nutrient removal and fine filtration.
-
Compact system reduces plant footprint by 25-40% compared to a conventional STP
-
These membranes are stated to be durable to ensure reliability and long membrane life, and low membrane replacement frequency.
-
The modular system is expandable.
-
Higher stability to organic shocks /upsets due to higher MLSS concentration.
-
The process operates under low suction, the ideal filtration method for small to large-scale membrane facilities, hence low power consumption.
-
Automated system makes the process operations easier to operate.
Disadvantages
-
Each vendor advocates his own criteria for the membranes and their types which makes it difficult to bring about a common and validated design criterion.
-
It is not possible to cannibalize the system between different manufacturers.
-
High reliance on energy input in the absence of bio methanation.
-
Patented process technology and decanters defying local cannibalization.
-
Detailed evaluation of existing plants required either by IITs, CPCB or NEERI.





 Web Mail : Info@atkinsindia.com
Web Mail : Info@atkinsindia.com Customer Care Number : +91 9992227788
Customer Care Number : +91 9992227788 Web Link : www.atkinsindia.com
Web Link : www.atkinsindia.com









