SBR- Sequencing Batch Reactors
This is a variant of Activated Sludge Process (ASP) technology & is essentially a batch treatment by combination of primary settling, aeration, secondary settling and decanting the treated sewage in a series of sequenced and or simultaneous reactions in the same basin on a time deferred cycle. Thus, among the multiple basins, one basin is used in one part of the cycle of aeration, settling and discharging the treated sewage in a cyclically repeated operation is done in another tank. Membrane of high efficiency fine bubble non-clog for diffused aeration is preferred.
Schematic flow diagram of Sequencing Batch Reactors process is presented
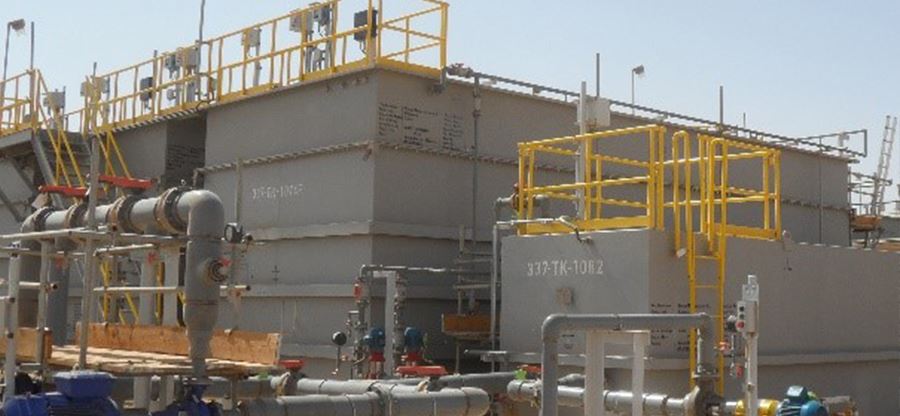
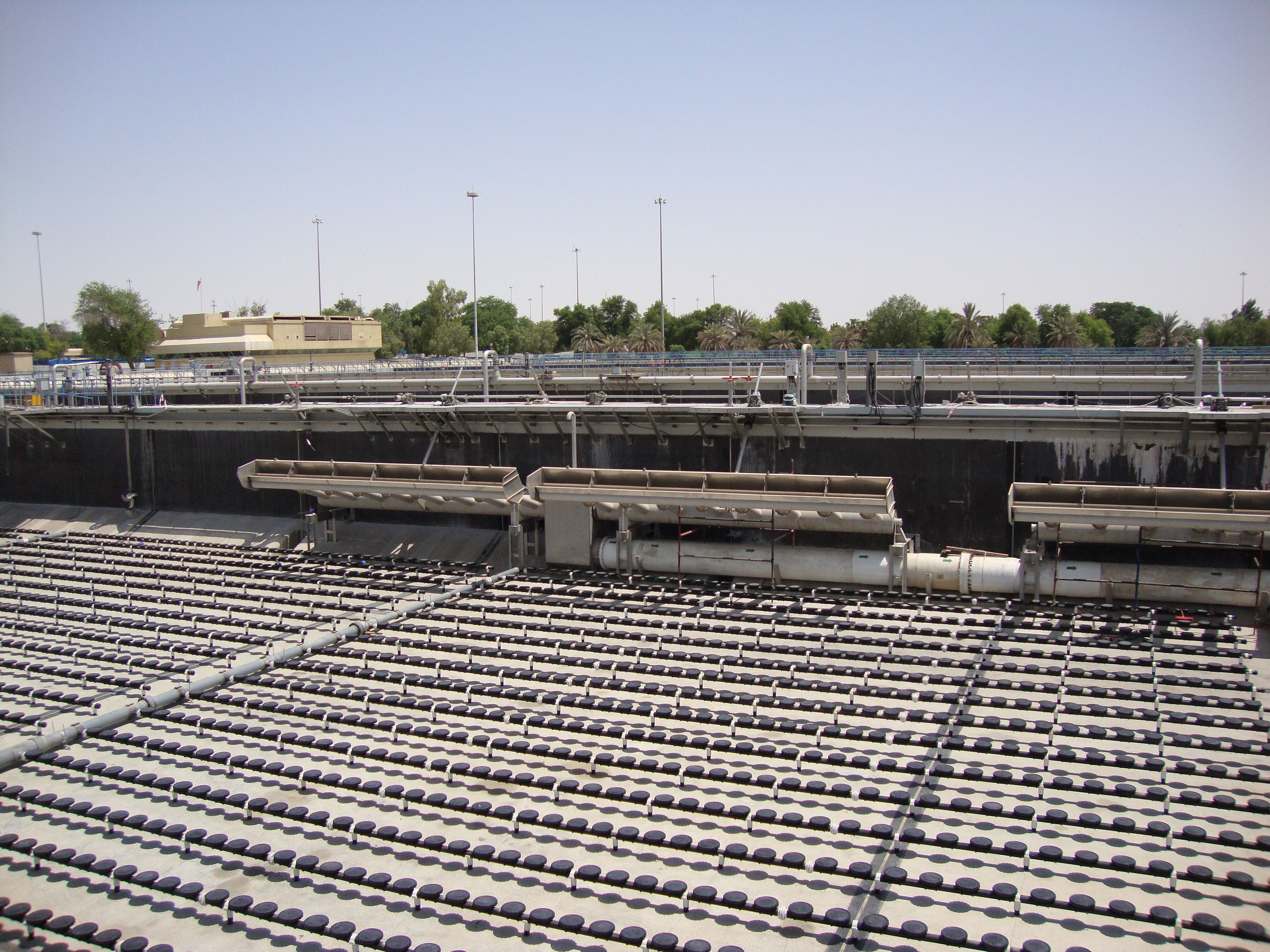
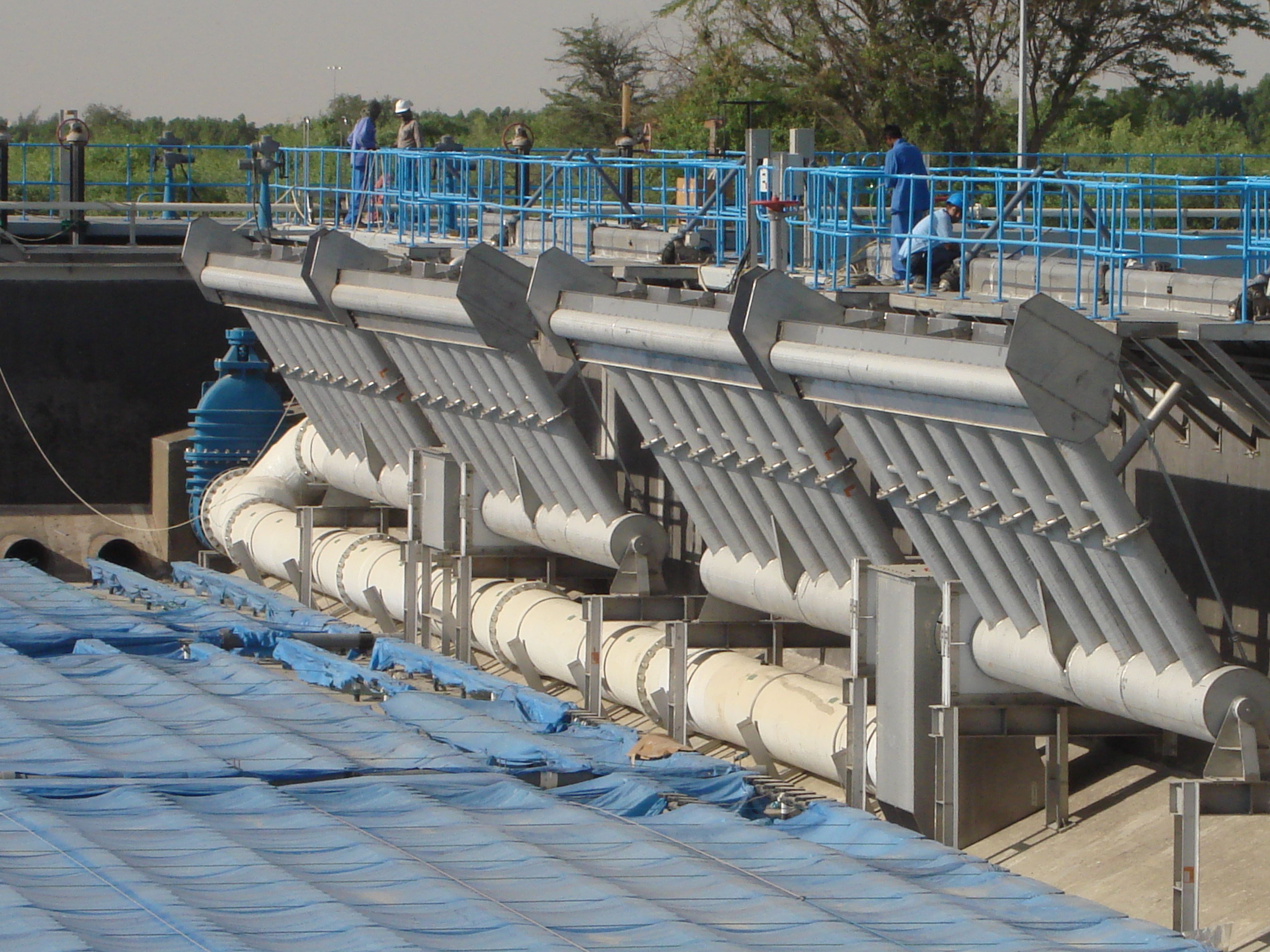




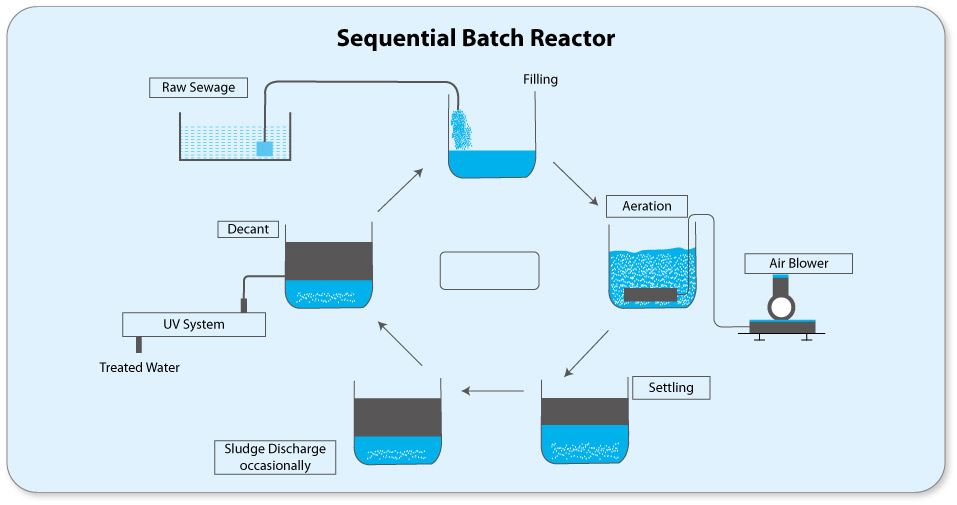
The essential components of SBR’s are:
-
Reactor basin
-
Waste sludge draw-off mechanism
-
Aeration equipment
-
Effluent decanter
-
Process control system
Advantages
-
The stabilized sludge is generated
-
Absence of odour and corrosive gases & can remove N and P concurrent with BOD.
-
Less manpower is required due to automatic control, easy operation & maintenance.
-
High quality effluent for reuse without separate nutrient removal and fine filtration.
-
Can be expanded as a modular system.
-
Capability to manage and treat variable loading conditions such as normal, dilute monsoon, diurnal and shock loads.
-
Can also be used with primary clarifiers and conventional F/M ratio for bio-methanation and energy recovery.
-
Separate secondary clarifiers and major return sludge pumping stations are not required, good use of common walls, simple square, rectangular or circular structures, can reduce the footprint compared to 5 conventional activated sludge process.
Disadvantages
-
At least semi-skilled manpower is required.
-
Patented process technology and decanters defying local cannibalization
-
No provision for sludge management
-
No provision of primary treatment to moderate pollution load variations.
-
Higher energy input if used without bio-methanation





 Web Mail : Info@atkinsindia.com
Web Mail : Info@atkinsindia.com Customer Care Number : +91 9992227788
Customer Care Number : +91 9992227788 Web Link : www.atkinsindia.com
Web Link : www.atkinsindia.com









